In choosing the best pocket knife you should pay particular attention to the type of steel used in the blade. Alongside edge geometry and design, blade steel is a critical element that determines how a knife performs. Steel is essentially an alloy (i.e. a mix) of carbon and iron that is often enriched with other elements to improve certain characteristics depending on the desired application.
In the knife industry different types of steel are created by varying the types of additive elements as well as how the blade is rolled and heated (i.e. the finishing process). Refer to our Knife Steel Composition Chart for more details on these elements.
Ultimately, the different types of steel used in knife blades each exhibit varying degrees of these 5 key properties:
Wear Resistance
Wear resistance is the steel’s ability to withstand damage from both abrasive and adhesive wear. Abrasive wear occurs when harder particles pass over a softer surface. Adhesive wear occurs when debris is dislodged from one surface and attaches to the other. Wear resistance generally correlates with the steel’s hardness but is also heavily influenced by the specific chemistry of the steel. In steels of equal hardness, the steel with larger carbides (think microscopic, hard, wear resistant particles) will typically resist wear better. However, carbides can become brittle and crack, thus decreasing toughness.
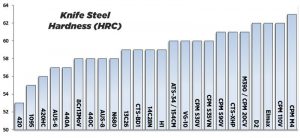
Hardness
Hardness is the ability to resist deforming when subject to stress and applied forces. Hardness in knife steels is directly correlated to strength and is generally measured using the Rockwell C scale (aka “HRC”)
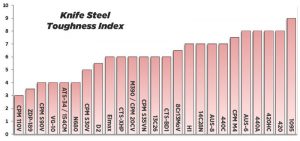
Toughness
Toughness is the ability to resist damage like cracks or chips when subject to impact or “sudden loads”. Chipping is a knife’s worst enemy and never easy to fix. There are a number of different ways to measure toughness (i.e. Charpy, Izod) thus it’s less standardized than hardness when it comes to knives. In general, the harder the steel the less tough it’s likely to be.
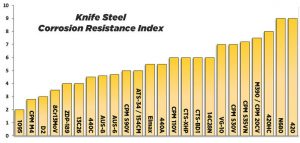
Corrosion Resistance
Corrosion resistance is the ability to resist corrosion such as rust caused by external elements like humidity, moisture and salt. Note that a high resistance to corrosion does involve a sacrifice in the overall edge performance.
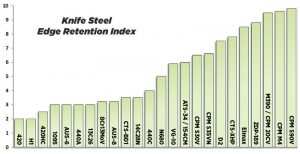
Edge Retention
Edge Retention represents how long the blade will retain its sharpness when subject to periods of use. It’s what everyone talks about these days but unfortunately the measurement of edge retention lacks any defined set of standards and so much of the data is subjective. For me, edge retention is a combination of wear resistance and an edge that resists deformation.